Nowadays, most batteries on the market are maintenance-free, which means they do not require the addition of water during their lifespan. These batteries use technology VRLA (Valve Regulated Lead Acid), designed for recombine the gases generated during charging and convert them back into water, avoiding electrolyte loss.
Main features of maintenance-free batteries:
- Sealed: They do not require adding water, since they do not lose electrolyte.
- Valve regulated: They have a safety valve that releases excess pressure if necessary.
- Safe and spill-free: They can be installed in different positions without risk of leakage.
- Long service life: Its technology minimizes water evaporation, increasing its duration.
Although maintenance-free batteries dominate the market, they are still sold maintenance-free batteries, which require periodic checks of the electrolyte level.
It is important to note that all batteries, even maintenance-free batteries, can benefit of certain maintenance practices to extend its useful life and ensure its optimal functioning
1 – VISUAL INSPECTION
- Check that the terminals are clean and free of corrosion.
- Check that there is no electrolyte leaks, cracks or swelling in the casing.
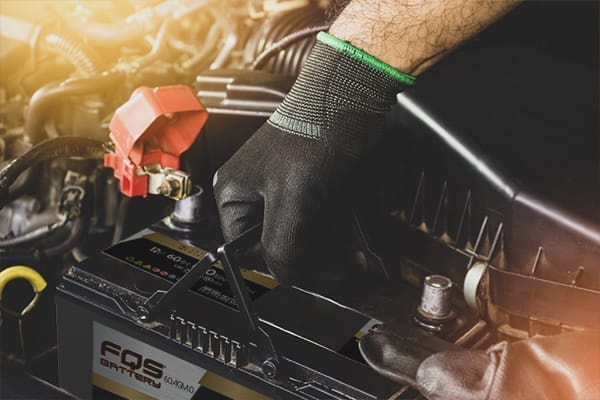
2 – TERMINAL INSPECTION
- If you detect sulfation (white or greenish deposits), clean them with a mixture of baking soda and water and a wire bristle brush.
- Apply petroleum jelly or dielectric grease to prevent corrosion.

3 – CHECKING THE ELECTROLYTE LEVEL (maintained batteries only)
Maintained lead-acid batteries require regular inspection of the electrolyte level to prevent damage and ensure performance.
Materials needed:
- Safety glasses and gloves.
- Screwdriver (if necessary to remove the covers).
- Distilled water (to refill if necessary).
Steps to follow:
- Safety first
- Make sure the car is off and parked on a stable surface.
- Wear gloves and safety glasses, as the electrolyte is corrosive.
- Access to the battery
- Locate the battery in the engine compartment.
- If it has a protective cover, remove it.
- Checking the electrolyte level
- If the battery is maintenance-free, remove the caps from each cell with a screwdriver.
- Observe the electrolyte level in each cell:
- It should cover the internal plates, but without exceeding the maximum mark.
- If the level is low and the plates are exposed, refilling is necessary.
- Filled with distilled water
- Use only distilled water, never tap water, as the minerals can damage the battery.
- Add distilled water to the proper level, without overfilling.
- Closing and cleaning
- Replace the plugs and make sure they are tightly closed.
- If there is any spillage, wipe it up with a dry cloth.
- Reinstall the battery cover if it was present.

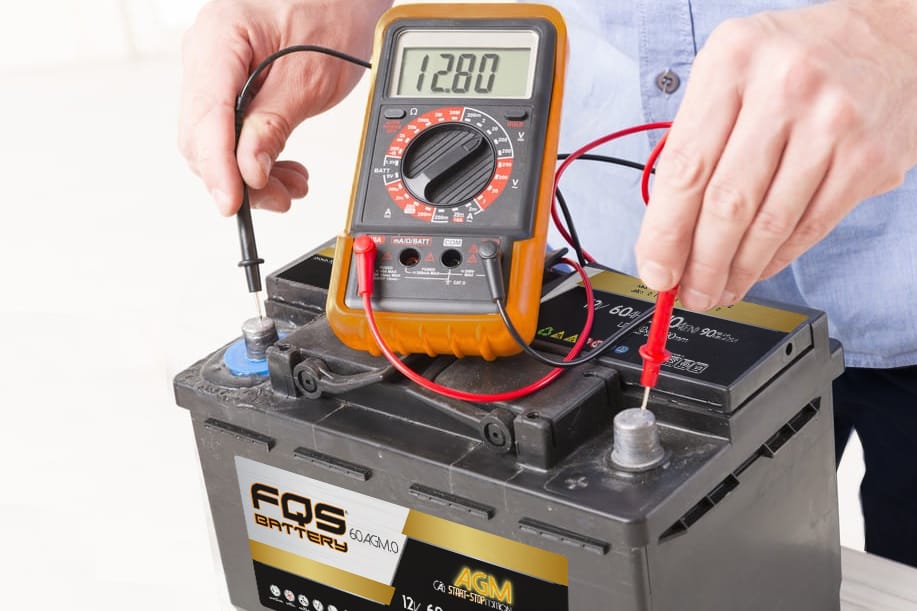
4 – CHECKING THE LOAD
- Use a multimeter To measure voltage with the engine off: must be between 12.4V and 12.8V.
- If the voltage is low, recharge the battery with a suitable charger before it is fully discharged.
Recommended reading: THE CORRECT USE OF A MULTIMETER.

5 – CHARGING SYSTEM REVIEW
- With the engine running, measure the charging voltage. It should be between 13.8V and 14.7V.
- If the alternator does not charge properly, the battery could be damaged prematurely.
6 – PROPER USE
- Avoid deep discharges, such as leaving the lights on with the engine off.
- If the vehicle will not be used for an extended period of time, disconnect the battery or use a load maintainer.
CONCLUSION
Both maintenance-free and maintenance-free batteries can benefit from proper care. maximize its lifespan and performanceBy following these recommendations, you'll avoid unexpected failures and ensure a reliable startup every time.
When was the last time you checked your battery?
Find our social media and leave your comment.
If you have any questions, please do not hesitate to contact us. FQS Battery, we will be happy to help you.





