Flooding has recently increased in frequency and severity, affecting thousands of vehicles in various regions. This phenomenon represents a considerable challenge for repair specialists, who must deal with the consequences of damage to various components, including batteries. Whether it's a 12V lead-acid battery, a lithium-ion battery, or a high-voltage system in electric vehicles, it's crucial to understand the risks and best practices for safe handling and assessment.
We have received several questions about FQS and we hope to be able to answer them in this article.
Impact of Floods on Batteries
Contact with water can significantly affect vehicle batteries, although the damage varies depending on the type:
Lead-Acid Batteries
12V lead-acid batteries are relatively water-resistant compared to other types, but they can still present problems such as:
- Corrosion on terminals and connectors, which reduces conductivity and performance.
- Dilution or contamination of the electrolyte, especially if the battery is not sealed.
- Possible short circuits if water enters the housing.
Lithium-ion batteries
Lithium batteries, used in hybrid and electric vehicles, can be seriously damaged if exposed to moisture:
- Sealing Commitment, which facilitates the entry of water and internal degradation.
- Internal short circuits and risk of thermal runaway, which can lead to overheating or fire.
- Corrosion of external connections, affecting its operational capacity.
High voltage batteries
In electric vehicles, high-voltage battery packs are protected by specialized housings, but they are not completely immune to flooding:
- Water ingress that can damage internal cells.
- Risk of thermal runaway, with a much higher energy potential than in smaller batteries.
- Retention of dangerous energy, which means that its handling requires extreme precautions.
Signs of damage to a battery after a flood
Before deciding whether a battery can be recovered or should be scrapped, it is important to look for signs of deterioration:
- Corrosion on terminals and connectors.
- Swelling or deformation of the casing.
- Discolored or unusual-smelling electrolyte (in lead-acid batteries).
- Burn marks or bulges on lithium-ion batteries.
- Water residue around the housing in high-voltage batteries.
- Errors in the vehicle's diagnostic system.

Procedure for handling flooded batteries
If a battery is confirmed to have been in contact with water, it is essential to follow appropriate protocols to minimize risks:
1 – Initial Safety Measures
- Use personal protective equipment such as gloves and safety glasses.
- Before handling the battery, check for any residual load with a multimeter.
- For high-voltage batteries, it is recommended to use specialized tools for deactivation.
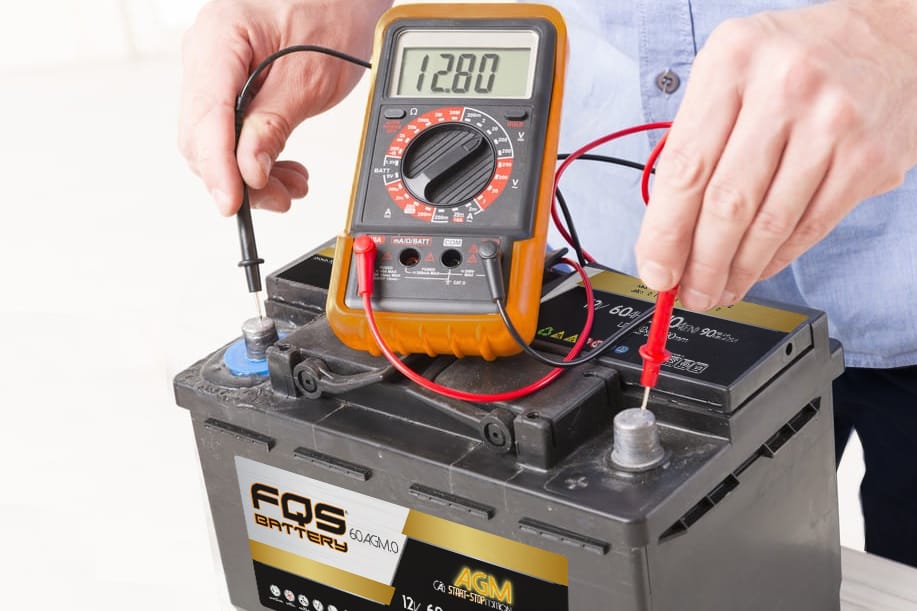

2 – Visual inspection and diagnosis
- Examine the external condition of the battery for obvious signs of damage.
- For high voltage lithium ion batteries, it is advisable to use advanced diagnostic tools to assess their integrity without opening them.
3 – Functional Tests
- In lead-acid batteries, the voltage and capacity.
- In high voltage lithium ion batteries, evaluate cell balancing and insulation resistance.
4 – Decision: repair or replacement
- Lead-acid batteries can be reconditioned in some cases by cleaning corrosion and recharging under controlled conditions.
- Lithium-ion and high-voltage batteries, due to their complexity and risk, typically require replacement rather than repair.

Responsible handling of damaged batteries
If a battery must be disposed of, it is vital to follow safe procedures:
- Transport them with caution to avoid short circuits or chemical leaks.
- Send them to specialized recycling centers for proper disposal.
- Follow local regulations to avoid negative environmental impacts.
CONCLUSION
The increase in vehicles affected by flooding poses a growing challenge for repair shops. Given the risk posed by damaged batteries, knowledge of their assessment, handling, and disposal is critical to ensuring the safety of both technicians and the environment. Adopting appropriate protocols and utilizing specialized diagnostic tools allows for informed decisions about a battery's viability after a flood. Careful handling and regulatory compliance are key to minimizing risks and optimizing the repair of these vehicles.